GCD Performance Analysis
In this article, I explain several methods for finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two integers and provide their implementations in Java. A performance comparison follows.
Euclidean algorithm
Recursive version:
int euclideanGcdRecursive(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) {
return a;
}
return euclideanGcdRecursive(b, a % b);
}
Iterative version:
int euclideanGcdIterative(int a, int b) {
while (b != 0) {
int temp = b;
b = a % b;
a = temp;
}
return a;
}
Binary GCD algorithm (Stein’s algorithm)
The following pseudocode is based on the algorithm described on this NIST page.
1. if a is 0 then return b
2. if b is 0 then return a
3. g = 1
4. while a is even and b is even
a = a/2
b = b/2
g = 2*g
(after this loop, at least one of a and b is odd.)
5. while a > 0
if a is even, a = a/2
else if b is even, b = b/2
else
c = |a-b|/2
if a < b, then b = c else a = c
6. return b*g
Here’s a straightforward Java implementation of the algorithm described above:
int binaryGcd(int a, int b) {
if (a == 0) {
return b;
}
if (b == 0) {
return a;
}
int g = 1;
while (a % 2 == 0 && b % 2 == 0) {
a /= 2;
b /= 2;
g *= 2;
}
while (a > 0) {
if (a % 2 == 0) {
a /= 2;
} else if (b % 2 == 0) {
b /= 2;
} else {
int c = Math.abs(a - b) / 2;
if (a < b) {
b = c;
} else {
a = c;
}
}
}
return b * g;
}
What can be optimized in this implementation? Division/multiplication by 2 operations can be replaced with binary shifts. Modulo operations involve division under the hood, so replacing the parts checking if a number is even (e.g. a % 2 == 0) with bitwise AND operation (e.g. (a & 1) == 0) sounds good. Applying those ideas, we get the following implementation:
int binaryGcdOptimized(int a, int b) {
if (a == 0) {
return b;
}
if (b == 0) {
return a;
}
int g = 1;
while ((a & 1) == 0 && (b & 1) == 0) {
a >>= 1;
b >>= 1;
g <<= 1;
}
while (a > 0) {
if ((a & 1) == 0) {
a >>= 1;
} else if ((b & 1) == 0) {
b >>= 1;
} else {
int c = Math.abs(a - b) >> 1;
if (a < b) {
b = c;
} else {
a = c;
}
}
}
return b * g;
}
And here’s a Java implementation of binary GCD algorithm based on the C++ implementation and optimization ideas from Daniel Lemire’s blog post.
int binaryGcdLemire(int a, int b) {
if (a == 0) {
return b;
}
if (b == 0) {
return a;
}
int trailingZerosA = Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(a);
int trailingZerosB = Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(b);
int shift = Math.min(trailingZerosA, trailingZerosB);
a >>= trailingZerosA;
do {
b >>= trailingZerosB;
int diff = b - a;
trailingZerosB = Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(diff);
if (diff == 0) {
break;
}
if (b < a) {
a = b;
}
b = Math.abs(diff);
} while (true);
return a << shift;
}
Denote that, Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(int) in Java is functionally equivalent to __builtin_ctz(unsigned int) in C++. They return the number of trailing zero bits in the binary representation of a given integer.
Guava’s implementation of binary GCD algorithm is as follows.
int gcd(int a, int b) {
/*
* The reason we require both arguments to be >= 0 is because otherwise, what do you return on
* gcd(0, Integer.MIN_VALUE)? BigInteger.gcd would return positive 2^31, but positive 2^31 isn't
* an int.
*/
checkNonNegative("a", a);
checkNonNegative("b", b);
if (a == 0) {
// 0 % b == 0, so b divides a, but the converse doesn't hold.
// BigInteger.gcd is consistent with this decision.
return b;
} else if (b == 0) {
return a; // similar logic
}
/*
* Uses the binary GCD algorithm; see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_GCD_algorithm. This is
* >40% faster than the Euclidean algorithm in benchmarks.
*/
int aTwos = Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(a);
a >>= aTwos; // divide out all 2s
int bTwos = Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(b);
b >>= bTwos; // divide out all 2s
while (a != b) { // both a, b are odd
// The key to the binary GCD algorithm is as follows:
// Both a and b are odd. Assume a > b; then gcd(a - b, b) = gcd(a, b).
// But in gcd(a - b, b), a - b is even and b is odd, so we can divide out powers of two.
// We bend over backwards to avoid branching, adapting a technique from
// http://graphics.stanford.edu/~seander/bithacks.html#IntegerMinOrMax
int delta = a - b; // can't overflow, since a and b are nonnegative
int minDeltaOrZero = delta & (delta >> (Integer.SIZE - 1));
// equivalent to Math.min(delta, 0)
a = delta - minDeltaOrZero - minDeltaOrZero; // sets a to Math.abs(a - b)
// a is now nonnegative and even
b += minDeltaOrZero; // sets b to min(old a, b)
a >>= Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(a); // divide out all 2s, since 2 doesn't divide b
}
return a << min(aTwos, bTwos);
}
Correctness of the GCD implementations
Before jumping into the performance analysis, let’s ensure that these six GCD calculation methods produce correct and consistent results. Unit tests will help achieve that.
import com.google.common.math.IntMath;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.CsvSource;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.ValueSource;
import java.util.Random;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
class GcdTest {
@ParameterizedTest
@CsvSource({
"48, 18, 6",
"100, 25, 25",
"17, 13, 1",
"1024, 512, 512",
"97, 89, 1",
"252, 105, 21",
"1071, 462, 21"
})
@DisplayName("Known GCD values")
void knownValues(int a, int b, int expectedGcd) {
assertEquals(expectedGcd, Gcd.euclideanGcdRecursive(a, b));
assertEquals(expectedGcd, Gcd.euclideanGcdIterative(a, b));
assertEquals(expectedGcd, Gcd.binaryGcd(a, b));
assertEquals(expectedGcd, Gcd.binaryGcdOptimized(a, b));
assertEquals(expectedGcd, Gcd.binaryGcdLemire(a, b));
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Edge cases")
void edgeCases() {
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(0, 5);
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(7, 0);
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(1, 100);
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(50, 1);
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(42, 42);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Random values")
void randomValues() {
Random random = new Random(12345); // Fixed seed for reproducibility
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
int a = random.nextInt(10000) + 1;
int b = random.nextInt(10000) + 1;
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(a, b);
}
}
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(ints = {2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024})
@DisplayName("Powers of 2")
void powersOfTwo(int power) {
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(power, power / 2);
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(power, power * 3);
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(power, 7);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Large numbers")
void largeNumbers() {
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(1000000, 999999);
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(524288, 262144);
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(999983, 999979);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Performance sanity check")
void performanceSanityCheck() {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE - 1);
assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults((int) Math.pow(2, 30), (int) Math.pow(2, 29));
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
assertTrue(duration < 1000, "GCD calculations took too long: " + duration + "ms");
}
private void assertAllMethodsReturnSameResults(int a, int b) {
int euclideanGcdRecursive = Gcd.euclideanGcdRecursive(a, b);
int euclideanGcdIterative = Gcd.euclideanGcdIterative(a, b);
int binaryGcd = Gcd.binaryGcd(a, b);
int binaryGcdOptimized = Gcd.binaryGcdOptimized(a, b);
int binaryGcdLemire = Gcd.binaryGcdLemire(a, b);
int guavaGcd = IntMath.gcd(a, b);
String message = String.format("GCD(%d, %d) - Methods disagree: euclideanGcdRecursive=%d, euclideanGcdIterative=%d,"
+ " binaryGcd=%d, binaryGcdOptimized=%d, binaryGcdLemire=%d, guavaGcd=%d",
a, b, euclideanGcdRecursive, euclideanGcdIterative, binaryGcd, binaryGcdOptimized, binaryGcdLemire, guavaGcd);
assertEquals(euclideanGcdRecursive, euclideanGcdIterative, message);
assertEquals(euclideanGcdRecursive, binaryGcd, message);
assertEquals(euclideanGcdRecursive, binaryGcdOptimized, message);
assertEquals(euclideanGcdRecursive, binaryGcdLemire, message);
assertEquals(euclideanGcdRecursive, guavaGcd, message);
}
}
Benchmarking with JMH
Benchmarking environment
OS : Linux 6.9.3-76060903-generic (amd64)
CPU : 12th Gen Intel Core i7-12700H (14 cores / 20 threads)
Max Frequency (MHz) : 4700.0000
JVM version : JDK 21.0.7, OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM, 21.0.7+6-Ubuntu-0ubuntu122.04
JVM options : -Xms1g -Xmx1g
JMH version : 1.37
Warmup : 3 iterations, 2 s each
Measurement : 5 iterations, 3 s each
Timeout : 10 min per iteration
Threads : 1 thread, will synchronize iterations
Benchmark mode : Throughput, ops/time
Benchmarking code setup
I use various types of test data for the performance benchmarking of those 6 GCD functions described so far. Small/medium/large numbers, mixed numbers i.e. combination of small, medium and large numbers, co-prime numbers, and numbers which are divisible by some power of 2.
import com.google.common.math.IntMath;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.Benchmark;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.BenchmarkMode;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.Fork;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.Level;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.Measurement;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.Mode;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.OutputTimeUnit;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.Param;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.Scope;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.Setup;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.State;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.Threads;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.Warmup;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@BenchmarkMode({Mode.Throughput})
@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.SECONDS)
@State(Scope.Benchmark)
@Warmup(iterations = 3, time = 2, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS)
@Measurement(iterations = 5, time = 3, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS)
@Fork(value = 3, jvmArgs = {"-Xms1g", "-Xmx1g"})
@Threads(1)
public class GcdBenchmark {
@Param({"SMALL", "MEDIUM", "LARGE", "MIXED", "COPRIME", "MULTIPLES_OF_POWERS_OF_TWO"})
private TestDataCategory testDataCategory;
private int[] aValues;
private int[] bValues;
private static final int TEST_PAIRS_COUNT = 1024;
private static final int[] PRIMES = generateFirstNPrimes(4_000);
private static final Random RANDOM = new Random(79);
@State(Scope.Thread)
public static class ThreadLocalIndex {
int index = 0;
}
@Setup(Level.Trial)
public void setup() {
aValues = new int[TEST_PAIRS_COUNT];
bValues = new int[TEST_PAIRS_COUNT];
System.out.printf("Setting up test data: %s (%s)%n", testDataCategory.name(), testDataCategory.getDescription());
switch (testDataCategory) {
case SMALL:
generateSmallNumbers();
break;
case MEDIUM:
generateMediumNumbers();
break;
case LARGE:
generateLargeNumbers();
break;
case MIXED:
generateMixedNumbers();
break;
case COPRIME:
generateCoprimeNumbers();
break;
case MULTIPLES_OF_POWERS_OF_TWO:
generateMultiplesOfPowersOfTwo();
break;
}
}
@Benchmark
public int euclideanRecursive(ThreadLocalIndex threadLocalIndex) {
int index = (threadLocalIndex.index++) & (TEST_PAIRS_COUNT - 1);
return Gcd.euclideanGcdRecursive(aValues[index], bValues[index]);
}
@Benchmark
public int euclideanIterative(ThreadLocalIndex threadLocalIndex) {
int index = (threadLocalIndex.index++) & (TEST_PAIRS_COUNT - 1);
return Gcd.euclideanGcdIterative(aValues[index], bValues[index]);
}
@Benchmark
public int binaryGcd(ThreadLocalIndex threadLocalIndex) {
int index = (threadLocalIndex.index++) & (TEST_PAIRS_COUNT - 1);
return Gcd.binaryGcd(aValues[index], bValues[index]);
}
@Benchmark
public int binaryGcdOptimized(ThreadLocalIndex threadLocalIndex) {
int index = (threadLocalIndex.index++) & (TEST_PAIRS_COUNT - 1);
return Gcd.binaryGcdOptimized(aValues[index], bValues[index]);
}
@Benchmark
public int binaryGcdLemire(ThreadLocalIndex threadLocalIndex) {
int index = (threadLocalIndex.index++) & (TEST_PAIRS_COUNT - 1);
return Gcd.binaryGcdLemire(aValues[index], bValues[index]);
}
@Benchmark
public int guavaGcd(ThreadLocalIndex threadLocalIndex) {
int index = (threadLocalIndex.index++) & (TEST_PAIRS_COUNT - 1);
return IntMath.gcd(aValues[index], bValues[index]);
}
private void generateSmallNumbers() {
for (int i = 0; i < TEST_PAIRS_COUNT; i++) {
aValues[i] = RANDOM.nextInt(100) + 1;
bValues[i] = RANDOM.nextInt(100) + 1;
}
}
private void generateMediumNumbers() {
for (int i = 0; i < TEST_PAIRS_COUNT; i++) {
aValues[i] = RANDOM.nextInt(10000) + 1;
bValues[i] = RANDOM.nextInt(10000) + 1;
}
}
private void generateLargeNumbers() {
for (int i = 0; i < TEST_PAIRS_COUNT; i++) {
aValues[i] = RANDOM.nextInt(1000000) + 1;
bValues[i] = RANDOM.nextInt(1000000) + 1;
}
}
private void generateMixedNumbers() {
for (int i = 0; i < TEST_PAIRS_COUNT; i++) {
switch (RANDOM.nextInt(3)) {
case 0 -> {
aValues[i] = RANDOM.nextInt(100) + 1;
bValues[i] = RANDOM.nextInt(100) + 1;
}
case 1 -> {
aValues[i] = RANDOM.nextInt(10_000) + 1;
bValues[i] = RANDOM.nextInt(10_000) + 1;
}
case 2 -> {
aValues[i] = RANDOM.nextInt(1_000_000) + 1;
bValues[i] = RANDOM.nextInt(1_000_000) + 1;
}
}
}
}
private void generateCoprimeNumbers() {
for (int i = 0; i < TEST_PAIRS_COUNT; i++) {
int indexOfPrime = RANDOM.nextInt(PRIMES.length - 3);
aValues[i] = PRIMES[indexOfPrime] * PRIMES[indexOfPrime + 1];
bValues[i] = PRIMES[indexOfPrime + 2] * PRIMES[indexOfPrime + 3];
}
}
private void generateMultiplesOfPowersOfTwo() {
for (int i = 0; i < TEST_PAIRS_COUNT; i++) {
int powerA = RANDOM.nextInt(20) + 1;
int powerB = RANDOM.nextInt(20) + 1;
int multiplierA = (RANDOM.nextInt(100) + 1);
int multiplierB = (RANDOM.nextInt(100) + 1);
aValues[i] = (1 << powerA) * multiplierA;
bValues[i] = (1 << powerB) * multiplierB;
}
}
private static int[] generateFirstNPrimes(int n) {
int[] result = new int[n];
int number = 2;
int index = 0;
while (index < n) {
if (IntMath.isPrime(number)) {
result[index++] = number;
}
number++;
}
return result;
}
public enum TestDataCategory {
SMALL("Numbers 1-100"),
MEDIUM("Numbers 1-10,000"),
LARGE("Numbers 1-1,000,000"),
MIXED("Mixed small/medium/large"),
COPRIME("Coprime pairs (GCD=1)"),
MULTIPLES_OF_POWERS_OF_TWO("Multiples of powers of 2");
private final String description;
TestDataCategory(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
}
}
Benchmarking results
Runtime: 38 minutes 9 seconds
Benchmark (testDataCategory) Mode Cnt Score Error Units
binaryGcd SMALL thrpt 15 80093873.958 ± 21598842.550 ops/s
binaryGcd MEDIUM thrpt 15 17819613.416 ± 4413404.244 ops/s
binaryGcd LARGE thrpt 15 9567475.056 ± 725753.987 ops/s
binaryGcd MIXED thrpt 15 20162041.959 ± 4193874.599 ops/s
binaryGcd COPRIME thrpt 15 8079315.863 ± 263211.444 ops/s
binaryGcd MULTIPLES_OF_POWERS_OF_TWO thrpt 15 35847878.254 ± 7404436.967 ops/s
binaryGcdLemire SMALL thrpt 15 250932146.168 ± 2115387.421 ops/s
binaryGcdLemire MEDIUM thrpt 15 108345918.881 ± 10938982.071 ops/s
binaryGcdLemire LARGE thrpt 15 28970832.010 ± 1344796.463 ops/s
binaryGcdLemire MIXED thrpt 15 113334606.186 ± 14236010.646 ops/s
binaryGcdLemire COPRIME thrpt 15 23301390.698 ± 239699.338 ops/s
binaryGcdLemire MULTIPLES_OF_POWERS_OF_TWO thrpt 15 249430736.491 ± 5927818.357 ops/s
binaryGcdOptimized SMALL thrpt 15 124634675.892 ± 5527667.667 ops/s
binaryGcdOptimized MEDIUM thrpt 15 25069070.741 ± 858523.595 ops/s
binaryGcdOptimized LARGE thrpt 15 12314533.497 ± 319010.967 ops/s
binaryGcdOptimized MIXED thrpt 15 24328557.052 ± 2182081.430 ops/s
binaryGcdOptimized COPRIME thrpt 15 9891866.846 ± 316097.230 ops/s
binaryGcdOptimized MULTIPLES_OF_POWERS_OF_TWO thrpt 15 31905618.950 ± 909187.425 ops/s
euclideanIterative SMALL thrpt 15 184124406.817 ± 619064.913 ops/s
euclideanIterative MEDIUM thrpt 15 67391615.575 ± 894162.038 ops/s
euclideanIterative LARGE thrpt 15 33709946.202 ± 211044.561 ops/s
euclideanIterative MIXED thrpt 15 74621091.918 ± 1309003.818 ops/s
euclideanIterative COPRIME thrpt 15 27762826.762 ± 75320.470 ops/s
euclideanIterative MULTIPLES_OF_POWERS_OF_TWO thrpt 15 177085933.434 ± 579951.675 ops/s
euclideanRecursive SMALL thrpt 15 171817766.717 ± 3601958.600 ops/s
euclideanRecursive MEDIUM thrpt 15 85117396.819 ± 2294969.999 ops/s
euclideanRecursive LARGE thrpt 15 43682280.831 ± 1568800.268 ops/s
euclideanRecursive MIXED thrpt 15 81862065.203 ± 711692.397 ops/s
euclideanRecursive COPRIME thrpt 15 36241379.984 ± 570170.584 ops/s
euclideanRecursive MULTIPLES_OF_POWERS_OF_TWO thrpt 15 168124256.670 ± 6360404.297 ops/s
guavaGcd SMALL thrpt 15 267479968.138 ± 435308.620 ops/s
guavaGcd MEDIUM thrpt 15 117407617.637 ± 487596.182 ops/s
guavaGcd LARGE thrpt 15 65493190.379 ± 2083317.443 ops/s
guavaGcd MIXED thrpt 15 107093681.790 ± 183118.261 ops/s
guavaGcd COPRIME thrpt 15 33155612.258 ± 3383485.098 ops/s
guavaGcd MULTIPLES_OF_POWERS_OF_TWO thrpt 15 277656366.472 ± 6692938.959 ops/s
The visualization below is generated via JMH Visualizer.
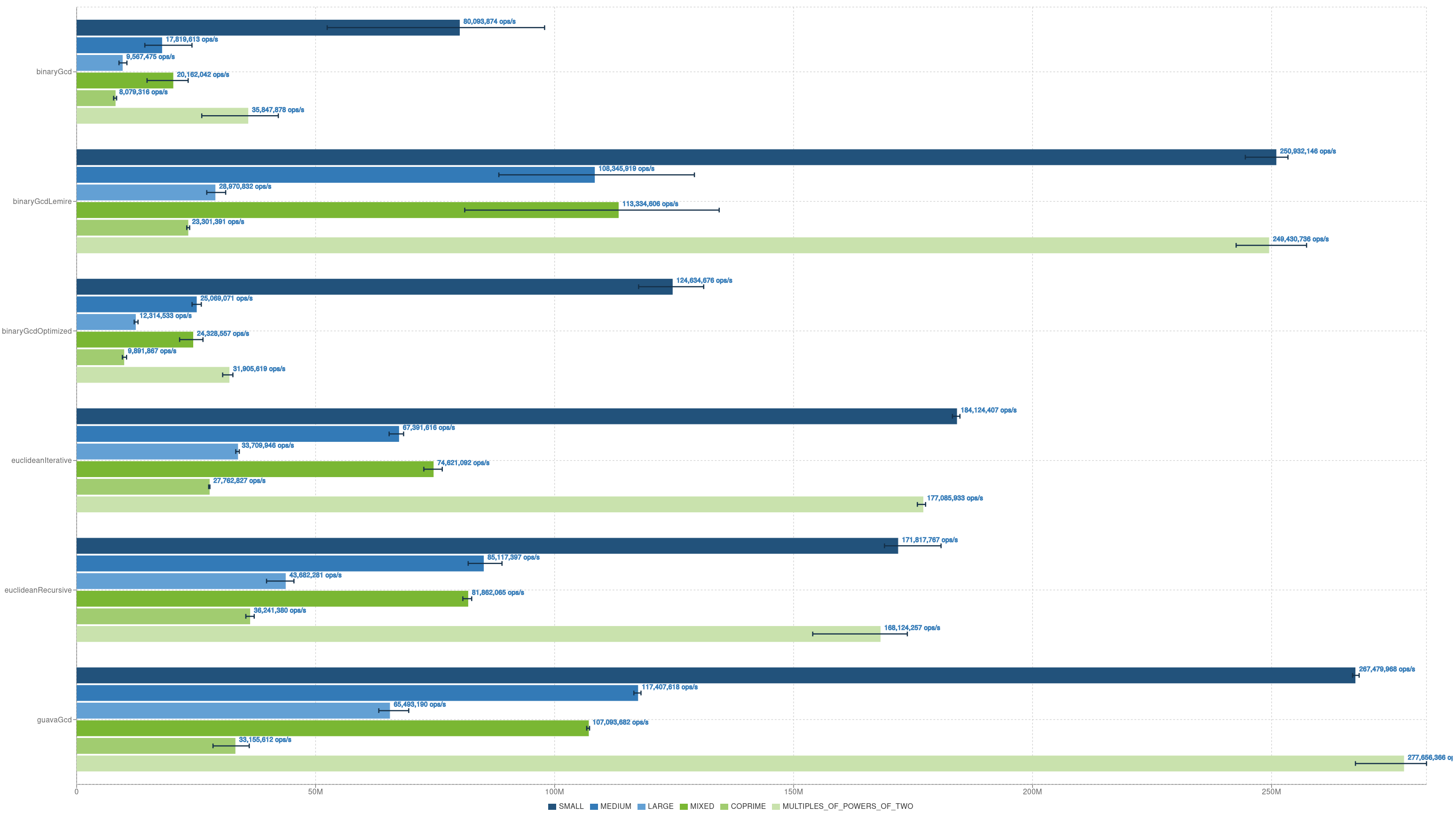
Conclusion
- Highly optimized binary GCD algorithms, i.e. Guava’s GCD and Lemire’s GCD achieve the highest throughput compared to the other GCD implementations. In general, Guava’s GCD is faster because it uses branchless techniques that improve CPU pipeline efficiency and branch prediction. It avoids some method calls and uses bitwise arithmetic that JIT compiles into fewer, faster instructions.
- Next, Euclidian GCD versions come. Notice that iterative and recursive versions of Euclidian GCD achieved close results. However, iterative version performs better. This can be explained with limited tail-call optimization (TCO) in JVM. The JVM doesn’t reliably perform tail-call optimization, which means recursive calls aren’t transformed into jumps internally. So recursive calls still accumulate stack frames and overhead.
- Plain binary GCD and its slightly optimized version achieved the lowest throughput. The optimized binary GCD performed better than the plain version due to reduced division and multiplication operations; nevertheless, both are nowhere near the performance of the other four GCD implementations.
- One final caveat: All of the GCD implementations above — except for Guava’s — do not check whether the given integer values are non-negative. I’ve omitted that check for simplicity, but ideally, the following lines can be added at the beginning of those methods:
a = Math.abs(a); b = Math.abs(b);